Many organizations are turning to virtual environments for their server needs due to their cost and efficiency. Instead of a room full of servers, virtual servers on hosted or in-house environments can perform the functions of multiple computers.
Avaya Messaging can be installed on a virtual environment enabling you to reuse the equipment you already have. Instead of buying a new computer to host the voice server, upgrades to existing hardware may be sufficient through virtualization.
|
Software |
Version |
|
VM Software |
VMware ESXi 4.x / 5.0 / 5.1 / 5.5 / 6.0 / 6.5 / 6.7 / 7.0 Hyper-V Server 2012 / 2016 Windows Terminal Services1 |
|
OS for Avaya Messaging |
Server 2012 R2 Server 2016 Server 2019 |
|
Note: ESXi has been tested on versions 4.x / 5.0 / 5.1 / 5.5 / 6.0 / 6.7 / 7.0. Hyper-V Server 2012 and Hyper-V Server 2016 have also been tested. |
|
Hardware |
|
|
CPU |
Requires Intel® CPU which meets or exceeds the requirements of ESXi 4+ |
1 - Windows Terminal Services only supports the installation of the client software. The Avaya Messaging server cannot be installed here.
Virtual Environment Limitations
Migrating data from a virtual machine environment is not supported.
Migrating data to a virtual machine from an existing physical environment is supported, but only if AM is installed first. Move an existing server onto a virtual machine by migrating the database using the utilities provided on the Messaging installation package. You can transfer both 7.x and 8.x systems to an 10.8 virtual environment. Messaging must be installed on a new virtual machine with a clean operating system.
|
Warning: Importing an existing Avaya Messaging environment to a virtual image is not supported. |
Avaya Messaging installed on a virtual environment requires the same hardware resource as non-virtual machine environments.
|
Note: The fax capability of Avaya Messaging within a virtual environment is limited to 24 ports. |
|
Warning: Do Not take snapshots while the servers are in operation as this can lead to serious corruption in the database. System performance may also be heavily compromised. To take a snapshot, shutdown the server first, then take the snapshot while the system is down. |
This table shows the list of VMWare features supported.
|
Feature |
Avaya Messaging 10.8 |
Avaya Messaging 11.0 |
|
Support for ESXi 6.0 |
Yes |
No |
|
Support for ESXi 6.5 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Support for ESXi 6.7 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Support for ESXi 7.0 |
No |
Yes |
|
VMware vMotion |
No |
No |
|
VMware Snapshot |
No |
No |
|
VMware HA |
Yes |
Yes |
|
VMware DRS |
No |
No |
|
VMware FT |
No |
No |
|
vSphere Standard Switch |
Yes |
Yes |
|
vSphere Distributed Switch |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Reservation Required |
No |
No |
|
VSAN Support |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Thin Provisioning |
No |
No |
Virtual Machine Environment Hardware Requirements
The hardware requirements for setting up Avaya Messaging within a virtual environment are the same as for a physical machine. See the System Requirements and Capacity chapter of this guide for more information.
The configuration of the virtual environment does create other considerations for server installation.
For further details on Hardware Requirements, see here.
VMware offers wide range of technologies which may be implemented on a virtual machine for greater redundancy and ease of maintenance. This section explains which features are compatible with the Avaya Messaging server application and how to utilize VMware solutions with Avaya Messaging in mind.
•High Availability: VMware also offers its own High Availability solution, which should not be confused with Avaya Messaging HA. VMware's HA model is initiated in 2 ways: one is hardware (machine) failure and the other is software (Operating System) failure. When the ESXi hardware fails on a system monitored by HA, VMware will automatically restart the Virtual Machine image on another ESXi host. If the OS becomes unresponsive, VMware HA will start the virtual machine on another ESXi host and bring the server back online. This will lead to down time while VMware moves operations onto another host. Avaya Messaging will be down during the recovery period and will not be able to answer calls until the secondary virtual image is fully up and running. The recovery occurs automatically, but it must be 'hard coded' to a specific recovery ESXi server. If there are no available resources on the recovery server, Avaya Messaging may fail to restart.
•Distributed Resource Scheduler: Distributed Resource Scheduler is intended for sites with multiple physical ESXi servers available. DRS keeps track of hardware resources, and is able to see the current availability of CPUs, RAM, etc. on all servers. When the main server crashes, DRS will automatically allocate the necessary resources and restart the virtual machine in a suitable environment. This means that Avaya Messaging will be guaranteed a minimum level of resources upon recovery to ensure there is no reduction in service. This is an advantage offered by DRS when compared to HA alone since HA does not consider hardware requirements when allocating space for a new virtual machine to replace the crashed server.
•Fault Tolerance: Fault Tolerance offers a higher level of protection than HA by eliminating of downtime. A virtual machine being monitored by an FT system will have a shadow image created that is identical to the monitored virtual machine. When the main server becomes unavailable for any reason, the shadow image which has been reproducing all activity on the main server will become active, instantly replacing the crashed server. This reduces the chance of an interruption or data loss in most active environments. However, due to the extensive nature of FT’s monitoring, FT can only support virtual machines with a single core CPU. This does not meet Avaya Messaging Voice Server’s minimum hardware requirements, so Avaya Messaging will remain incompatible with FT until the algorithm is changed to support the resources required.
VM Environment Feature Comparison Chart
|
|
HA |
DRS |
FT |
|
Active Migration |
N |
N |
N |
|
Recovery from Hardware Crash |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Recovery from Software Crash |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
0 Down Time during Crash |
N |
N |
Y |
|
Smart Allocation of Hardware Resources |
N |
Y |
N |
|
Avaya Messaging Support |
Y |
Y |
N* |
|
Known Behaviors: |
|||
|
Voice Traffic |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
N/A* |
|
iLink Pro Desktop |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
N/A* |
|
Messaging |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
N/A* |
|
CTI |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
Interrupted until HA recovers |
N/A* |
* Due to the way in which Fault Tolerance is designed, Avaya Messaging cannot function within the FT model. FT is limited with regard to computer resources (e.g. single core processor) while Avaya Messaging has specific minimum resource requirements to function properly. Until VMware upgrades the FT system to support higher amounts of resources, Avaya Messaging cannot be deployed under the FT model.
VMware: HA for the Consolidated Server
In a High Availability environment, the Primary and all Secondaries act as backups for each other. If one server fails, the Consolidated server redirects traffic through the remaining operational units preventing any service interruptions. However, the Consolidated server has no such protection. If the Consolidated server fails, the entire system will fail.
VMware includes an HA option for its Hosts, providing failover support for the Consolidated server. Both the Consolidated and Primary voice servers can backed up this way. The Secondary voice servers cannot.
1.The site admin must install and configure VMware vSphere on the network. There should also be an external SAN for data storage.
2.Create a Cluster within vSphere.
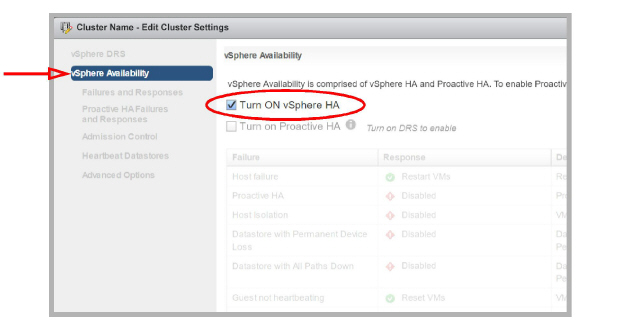
•When configuring the Cluster, under vSphere Availability, ensure that Turn ON vSphere HA is enabled.

3.Add 2 or more Hosts within the Cluster. One Host contains the virtual machine that houses the Consolidated server, while the others are available should the active Host fail.
|
Important: It is essential that all of the Host servers (Consolidated, Primary, and backups) have their clocks synchronized. Certain critical functions within Avaya Messaging are time sensitive and will fail if the Hosts are not coordinated. |
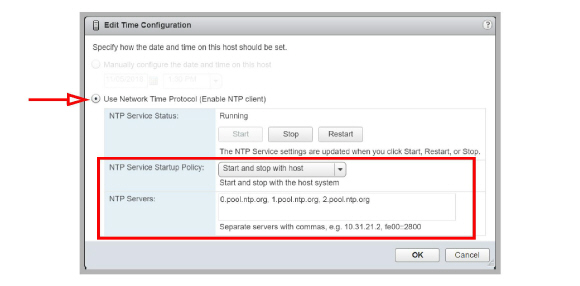
4.For each Host, open the Configuration tab and go to System > Time Configuration.
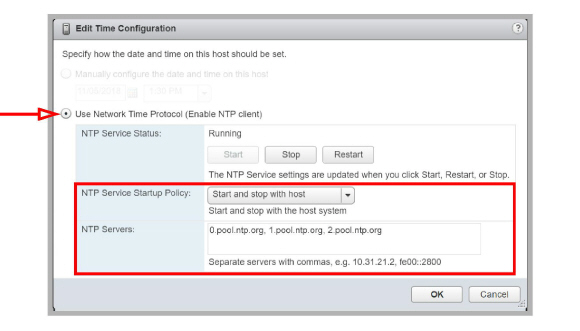
•Enable Use Network Time Protocol (Enable NTP client).
•Set the NTP Service Startup Policy to Start and stop with host.
•Enter one or more NTP servers in the space provided. The time signals will be synchronized with these sites.
•Start / Restart the NTP Service to activate the changes.
5.Create virtual machines and choose the SAN as the data storage location.
6.Edit the settings for each virtual machine.
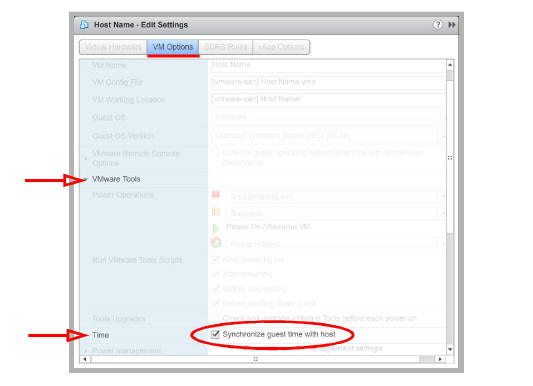
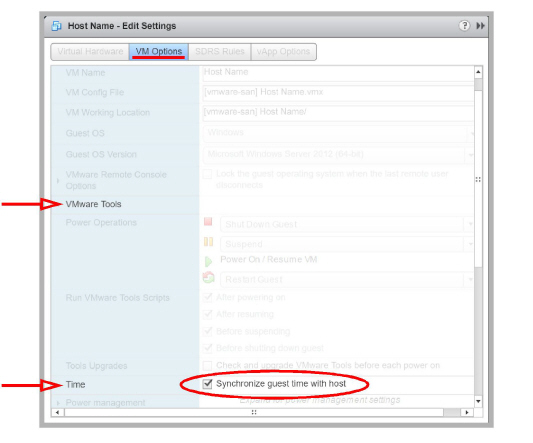
Under VM Options > VMware Tools > Time, enable Synchronize guest time with host.
7.Install the Avaya Messaging Consolidated server onto one of the virtual machines.
If the Host with the virtual machine running the Consolidated server fails, VMware will automatically move the server to another Host within the Cluster and restart the virtual machine.
|
Important: The Avaya Messaging system will be unavailable during the changeover and reboot process. |
VMware: HA for the Primary Voice Server
In a High Availability environment, the Primary and all Secondaries act as backups for each other. If one server fails, the Consolidated server redirects traffic through the remaining operational units preventing any service interruptions.
VMware includes an HA option for its Hosts, providing failover support for the Primary voice server. Both the Consolidated and Primary voice servers can backed up this way. The Secondary voice servers cannot.
1.The site admin must install and configure VMware vSphere on the network. There should also be an external SAN for data storage.
2.Create a Cluster within vSphere.
•When configuring the Cluster, under vSphere Availability, ensure that Turn ON vSphere HA is enabled.
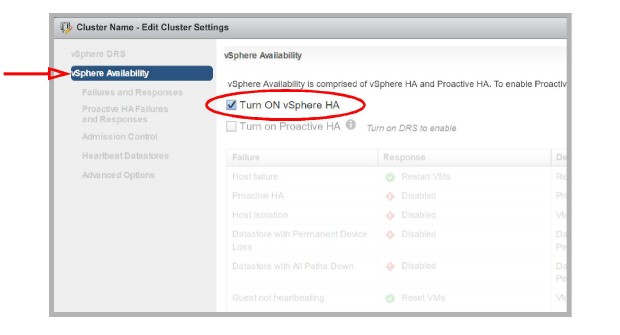
3.Add 2 or more Hosts within the Cluster. One Host contains the virtual machine that houses the Primary voice server, while the others are available should the active Host fail.
|
Important: It is essential that all of the Host servers (Consolidated, Primary, and backups) have their clocks synchronized. Certain critical functions within Avaya Messaging are time sensitive and will fail if the Hosts are not coordinated. |
4.For each Host, open the Configuration tab and go to System > Time Configuration.
•Enable Use Network Time Protocol (Enable NTP client).
•Set the NTP Service Startup Policy to Start and stop with host.
•Enter one or more NTP servers in the space provided. The time signals will be synchronized with these sites.
•Start / Restart the NTP Service to activate the changes.
5.Create virtual machines and choose the SAN as the data storage location.
6.Edit the settings for each virtual machine.
Under VM Options > VMware Tools > Time, enable Synchronize guest time with host.
7.Install the Avaya Messaging Primary voice server onto one of the virtual machines.
If the Host with the virtual machine running the Primary voice server fails, VMware will automatically move the server to another Host within the Cluster and restart the virtual machine.
|
Important: The Avaya Messaging system will be unavailable during the changeover and reboot process. |
Additional Considerations for AACC Users
There are additional conditions for sites that are integrating with Avaya Aura Contact Center.
•The Avaya Messaging virtual machine must use the same network interface card (NIC) for both ELAN and CLAN
•On the CS1000, configure the parameter Set Type = 2008 for the DMG ports.
•Configure the following 2 services for Automatic (Delayed Start):
UC Voice Server
UC Service Recovery Manager (found on the Consolidated Server)
Virtual Environment Deployment Example
The following are performance results from a virtualized Avaya Messaging system running 100 active voice ports with 1,000 users registered under the system. Please keep in mind that this is a limited test run to showcase how a typical operation may perform under a virtual environment. This example does not guarantee an identical level of performance on every virtual environment, but rather serves as a guideline with regards to Avaya Messaging’s behavior under virtual environments.
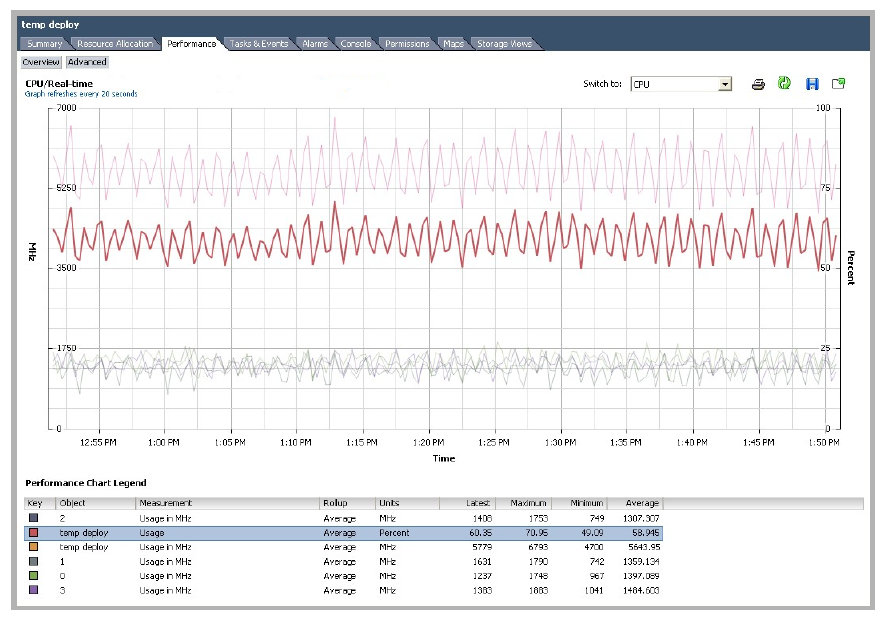
Avaya Messaging used an average of 58.945% of the CPU capacity, which equates to 5,643.95 MHz. When considering the Maximum requirement, providing at least 6.8 GHz of CPU resources to Avaya Messaging will guarantee a consistent level of performance.
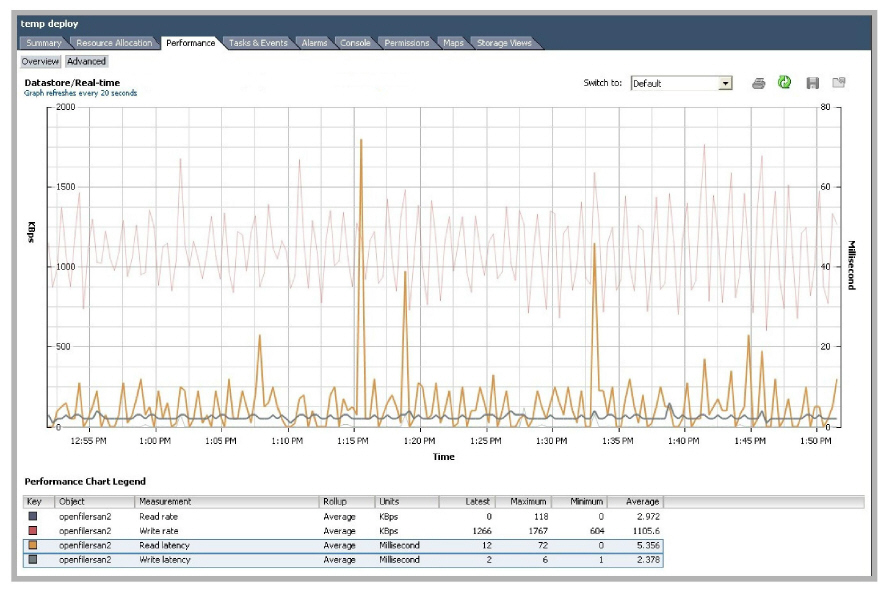
Avaya Messaging achieved a low average latency of 5.356ms for reading and 2.378ms for writing.
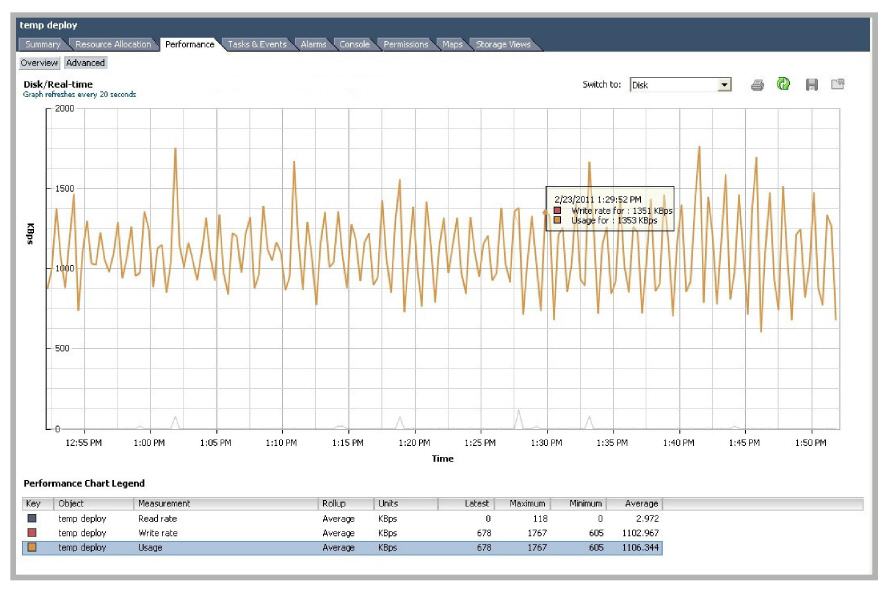
Avaya Messaging had an average disk usage rate of 1,106.344 KBps with a peak of 1,767 KBps. Ensuring a data transfer rate of 1,800 KBps to Avaya Messaging will guarantee a consistent level of performance.
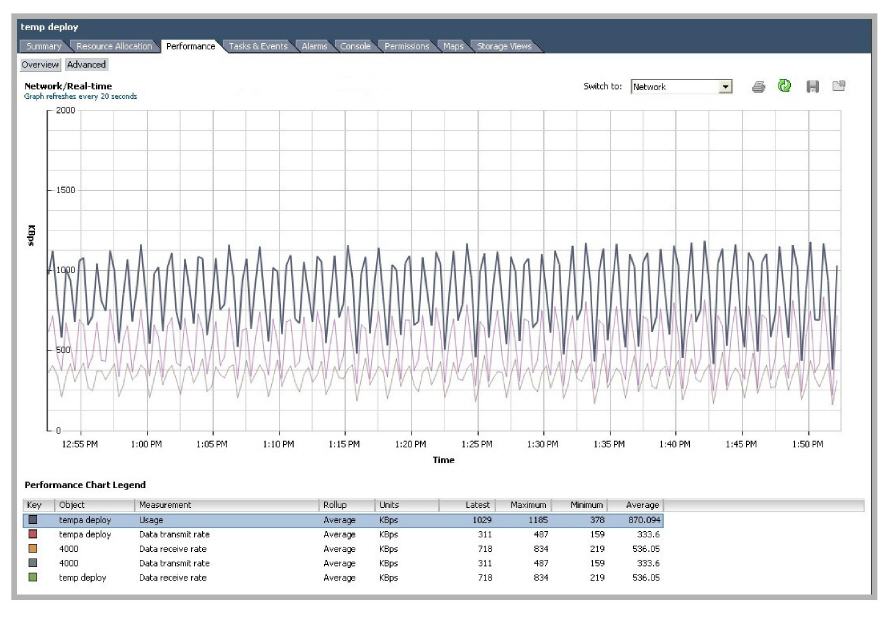
Avaya Messaging had an average network usage rate of 870.094 KB/s with a peak of 1,185 KB/s. Providing 1,500 KB/s of network bandwidth to Avaya Messaging will guarantee a consistent level of performance.
Since Avaya Messaging is designed to be the sole application running on a given Virtual Machine, it is easy to assign the necessary resources for Avaya Messaging. By ensuring that Avaya Messaging always has access to the required resources, you will be able to guarantee the level of performance required by your site.