Optimizing Network Traffic with Multiple Adapters
In a typical environment, there are 2 types of traffic that are generally present on a Messaging server:
•Voice traffic - Voice traffic refers to all information exchanged from the communication network that is connected to Messaging.
•Data traffic - Messaging exchanges information with other data servers to perform its tasks as a Unified Communications server. This data includes: email synchronization, database synchronization in High Availability systems, client access via web, desktop and mobile clients, SMTP, IMAP, LDAP and other types of data traffic.
Servers with multiple network adapters can optimize their network traffic by creating a division between the voice and data traffic. Voice (and fax) represents real time data exchange and as real time information, requires its traffic to be prioritized. This document discusses the methods available to IT departments to optimize the traffic between the two types of data.
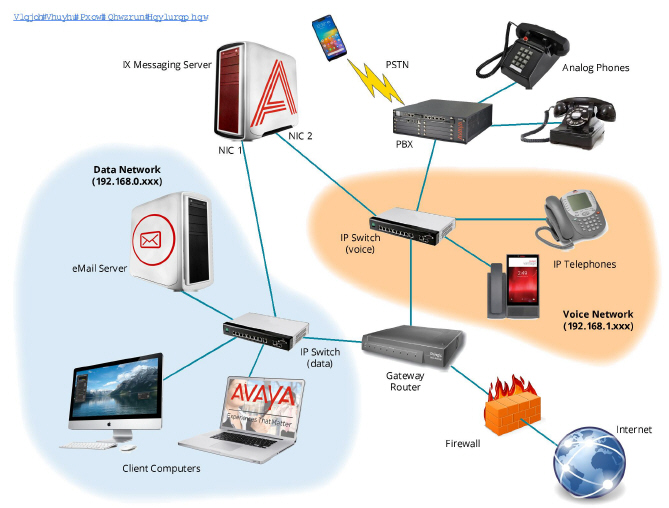
Environments with multiple subnetwork addresses
In many environments, their voice traffic is on a separate subnetwork. For example, data traffic resides on 192.168.0.x and voice traffic resides on the 192.168.1.x subnetwork. In this case, the simplest way to direct network traffic is to assign one network adapter to the 192.168.0.x subnetwork and one network adapter to the 192.168.1.x subnetwork. In this example, the VoIP PBX or Gateway should be on the same subnetwork as the voice adapter on 192.168.1.x. Since Messaging applications will try to connect via TCP to their destination via the Windows TCP stack, preference will be automatically given to the network adapter within the subnetwork that the application is trying to reach. This will isolate the Messaging applications’ attempts to connect to the VoIP end point to the network adapter within the same subnetwork. Visual examples of both single server and high availability implementations of multiple network adapter configurations are shown below.

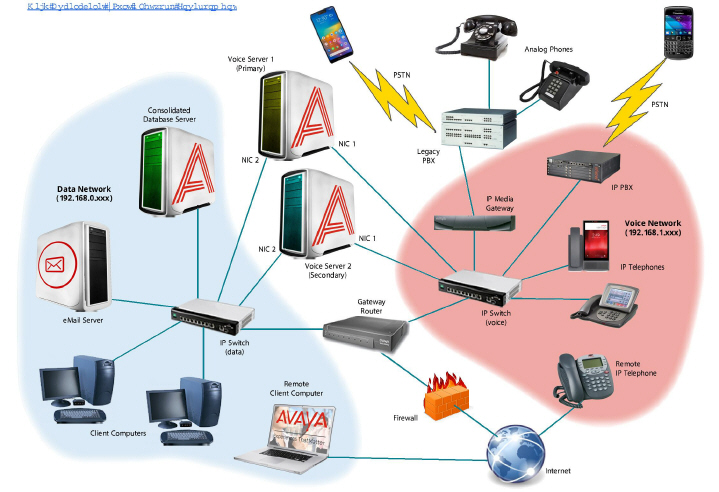
Binding SIP voice traffic to one network adapter
Messaging allows you to bind a specific adapter to the SIP application layer. This can be done by:
1.Open the ETSIPSERVICE.INI file.
2.Find the line that states Internal IP =
3.The default value is DETECT. Change this to the physical address of the network adapter to be bound
(e.g. 192.168.1.100).
4.Save the file.
5.Open Service Control Manager.
6.Locate and STOP the UC SIP Service.
|
Note: Any active calls will be disconnected when you stop this service. Choose a time when traffic loads are low to limit the impact of making this change. |
7.The service will automatically restart.
The SIP endpoints (PBX, Media Gateway, etc.) should be configured on the voice subnetwork IP range only to avoid any cross routing between networks and thus defeating the purpose of separate adapters.
Ensuring application data separation
To ensure the use of a separate adapter, the application servers and clients must be configured to use the corresponding subnetwork intended for data use. Relevant configuration parameters are listed below.
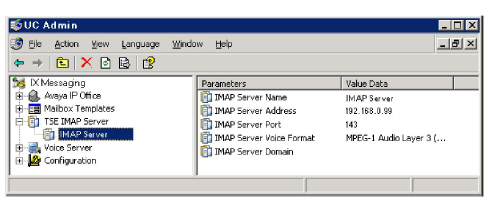
email (IMAP) Synchronization
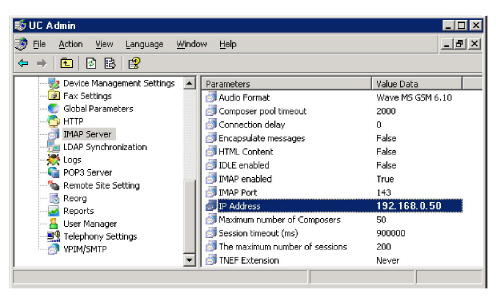
Ensure that the IMAP server intended for configuration resides on the same data network as the intended data NIC (our example uses the 192.168.0.x subnetwork). The image below shows an example configuration of a data network configured IMAP server.
If your IMAP server resides on another network or across the Internet, ensure the default gateway for the UC server resides on the data network and is configured for the data NIC only (voice NIC default gateway configuration should be left blank).
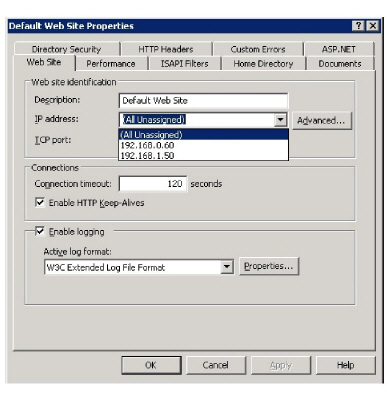
Connecting to Web Access
Verify that the IIS Website IP Address setting is configured to the data subnetwork as shown below on the web site properties dialog box, and that all DNS entries and client access attempts are directed to this IP address.
Desktop Clients (iLink Pro Desktop)
Ensure that all clients are configured to connect to the UC server via the data network address (our example uses the 192.168.0.x subnetwork). If connecting externally, ensure all relevant NAT, DNS and Routing entries direct requests to the data network IP address.
Mobile Clients
Similar to the desktop clients, all UC Mobile clients should be directed to the data network IP address. If connecting externally, ensure all relevant NAT, DNS and Routing entries direct requests to the data network IP address.
SMTP, IMAP, LDAP and others
The following fields should be setup to only use the data subnetwork as well.
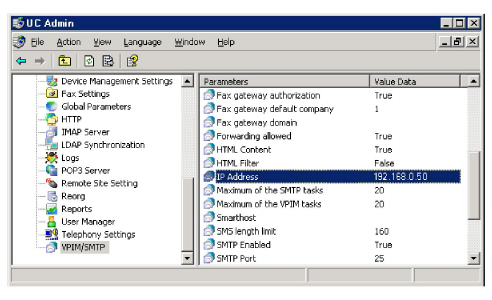
VPIM/SMTP:
IMAP Server:
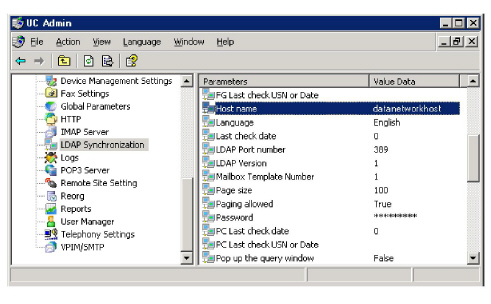
LDAP Synchronization Host Name:
Company Domain Name/IP Address:
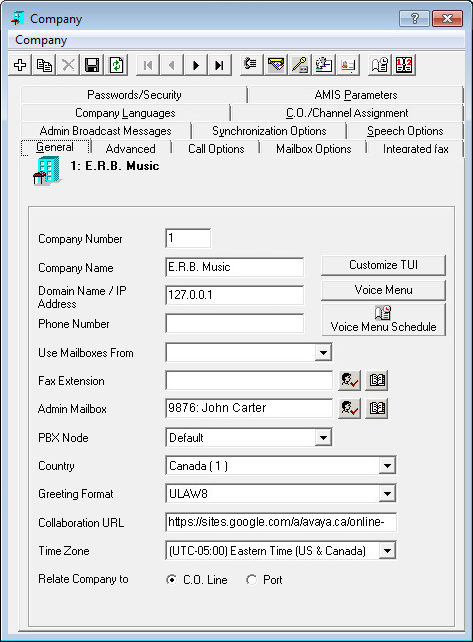
This ensures that all relevant UC Communication and non-voice protocols are transmitted via the data network rather than voice.
|
Note: Microsoft does not recommend assigning multiple network adapters to the same physical network and subnet. Please refer to the link below. |
|
Note: To read about Network adapter teaming and server clustering refer to the link below. |
|
Note: To read about configuring your server for network load balancing, please refer to the link below. |