
Vulnerability of the Single Server System
The High Availability system is designed to deliver a redundancy solution to environments where uptime is critical. The HA system achieves redundancy through Secondary servers that are constantly online along with the Primary server. In a traditional single server environment as shown below, the system is vulnerable to downtime which can be caused by the malfunction of the single Voice Server computer.

Since only one Voice Server is operating, any failure of the voice server equates to downtime. Even regular tasks such as regular maintenance, or a simple reboot will cause the system to be offline in single server configurations.
Reliability of the Multi-Server System
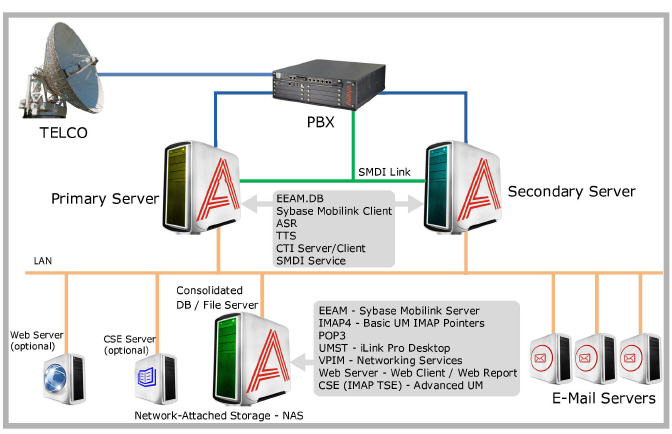
In the multiple server environment illustrated below, the Primary server is supported by the Secondary server(s) at all times. This means that a site can remain functional even if one of the voice servers fail. When the Primary server stops working, a Secondary server will take over until the Primary is back online.
The Primary and Secondary servers are able to work in unison with the help of the Consolidated (DB/File) server, also refereed to as the Common server. The Consolidated server manages the flow of data between all servers, and ensures proper synchronization of files. For a detailed explanation on database synchronization, please refer to Database Management on page 83, Failure Scenario on page 84 and Recovery Scenario on page 85.
While the Multi-Server installation guarantees uptime for the voice servers, there may be scenarios in which the PBX itself is out of service.
Multiple Server Multiple PBX System
The multiple server system combined with multiple PBXs provides the most reliable configuration. In this scenario, maximum uptime is guaranteed even if the PBX fails along with the Primary server. The secondary PBX and the Secondary server will continue to accept calls while the Primary voice server and the primary PBX are offline.

In a High Availability environment, the databases in all the servers are synchronized through the Sybase Mobilink system. The Consolidated (Common) server acts as the Mobilink Server and manages the database for all of the Primaries and Secondaries.
This architecture gives sites full message access at all times, not just full uptime for all Voice server functions. Whenever a change (new message, deleted message, etc.) is made in either the Primary or Secondary servers, the Consolidated server copies these change to all databases in the system, allowing end users to maintain their messages and greetings even when one of the servers become unavailable.

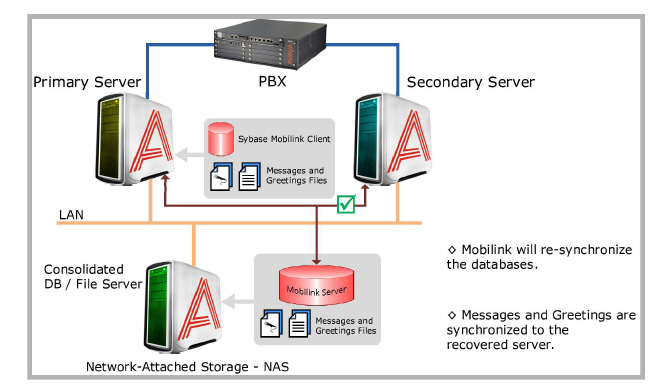
In this scenario, the Secondary server is unavailable due to a malfunction, severing the tie between the databases. The new messages received in the Primary server will continuously be synchronized with the Consolidated server but the Secondary server will be left behind during the down time.
Any messages received by the Secondary server are still accessible by the users since the database has already been synchronized before the Secondary server crash. There is also no disruption in regular service since the Primary server is still fully functional. All traffic is handled by the Primary server in the meantime.

In this scenario, the Secondary server that was down in the previous example has recovered. Soon after the Secondary server comes back online, the Consolidated server will start to synchronize the data between all the servers again, allowing the Secondary server to catch-up to the current database.
All messages and greetings will become automatically up to date on the secondary system soon after it comes online, which means that recovery will be a virtually invisible process that takes place in the background during regular operation.
The High Availability system utilizes a unique licensing feature that allows full functionality of service while only one server holds the Sentinel key. In all cases, the Primary server will hold the USB Sentinel and becomes the primary holder of the license. However, the license file will be copied to all servers in the system through the database synchronization performed by Sybase Mobilink.
The copied license files will allow other servers (other than the Primary) to maintain full functionality even when they don’t have individual license available to them. This system also allows for easier license management since only the Primary server has to be updated, should there be any type of addition or modification to the license.
However, the copied license files are time stamped to expire after a certain period. The time stamps are constantly updated by the Primary server, so it will not have any effect during regular operation.

License Management During Primary Server Down Time
When the Primary server becomes unavailable, it will also stop updating the time stamps on the copied license files that exist on the Secondary server and the Consolidated server. When this happens, the Primary server has to be recovered within 7 days. If the Primary server isn’t brought back online within the 7 days, the copied license files will expire and the system will cease to function due to invalid license status.
Since 7 days is a generous time period for recovery, most sites will not even notice such architecture in licensing. They will experience no problems as long as the Primary server is recovered in a timely manner.

High Availability Redundancy & Scalability
Server Specification
The minimum configuration for a High Availability system is three servers, Primary, Secondary and Consolidated.
As of now, the High Availability system is able to support up to 20 voice servers maximum. This means that a site can maintain 1 Primary server and 19 Secondary servers in a single High Availability environment.
Configuration Limitation
Each voice server is designed to support up to 120 ports (SIP).
A single High Availability environment can support up to 20,000 user accounts (business rules apply).
Single Web server can support up to 10,000 users.
Single CSE server can support up to 5,000 users.
Other Rules and Limitations
The system is high availability rather than fully redundant.
The MWI function is only available for Voice and Fax messages.
|
Warning: Avaya Messaging is not compatible with Windows Remote Desktop Services 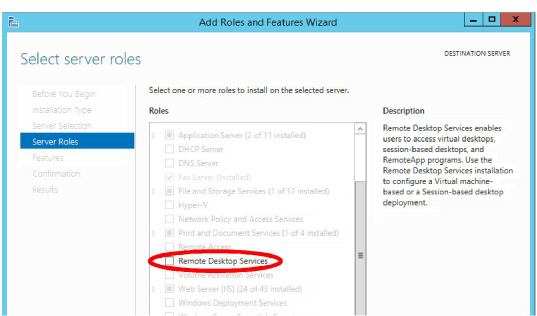
|
High Availability Configuration Flow
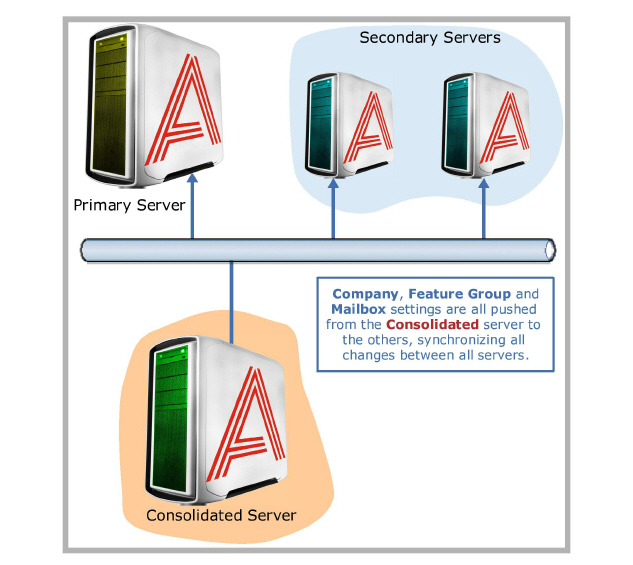
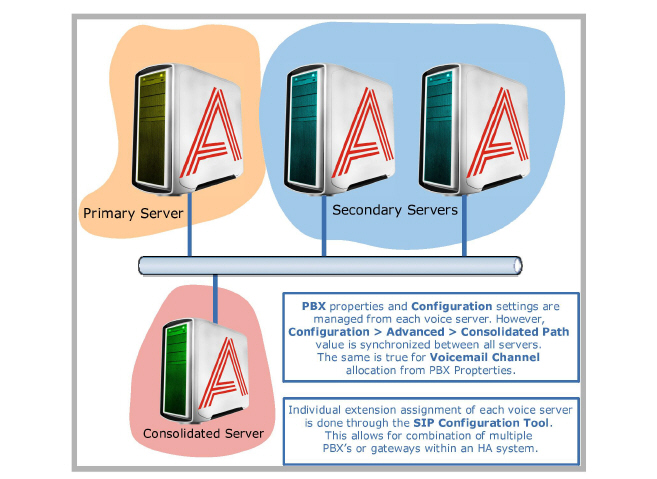
Most configurations within an HA system will take place on the Consolidated server. While all servers have access to Messaging admin console, only the Consolidated server has the ability to change the fields for Company, Feature Group and Mailbox settings. Any changes made on these fields from the consolidated server will be pushed to all voice servers, which synchronizes configuration settings on all servers.
PBX properties and Configuration section within Messaging admin console is managed individually. Since each voice server may integrate into a different PBX, it is necessary for voice servers to be in control of their PBX related settings. However, Configuration > Advanced > Consolidated Path will be synchronized between all servers. This is the path which defines the location of the Consolidated server, so all servers must have an identical entry to correctly synchronize. The same goes for the Voicemail Channel list within the PBX. This list will be a compilation of all channels allocated on all voice servers. Defining individual extensions or channels within a voice server is done through the SIP Configuration Tool, which manages each voice server separately.
Requirements for High Availability Installations
In addition to all of the normal specifications, High Availability installations have several other requirements that must be met:
•All servers must be part of the same domain.
•All servers must have a minimum 1 GB/s connection to the network.
•The maximum round-trip latency between the servers must be no more than 10 ms.
•The maximum round-trip latency between the voice servers and the PBX must not exceed 200 ms.
Optimal round-trip latency is less than 150 ms.
•The path of connectivity must have 1.5 MB/s guaranteed bandwidth with no steady-state congestion.
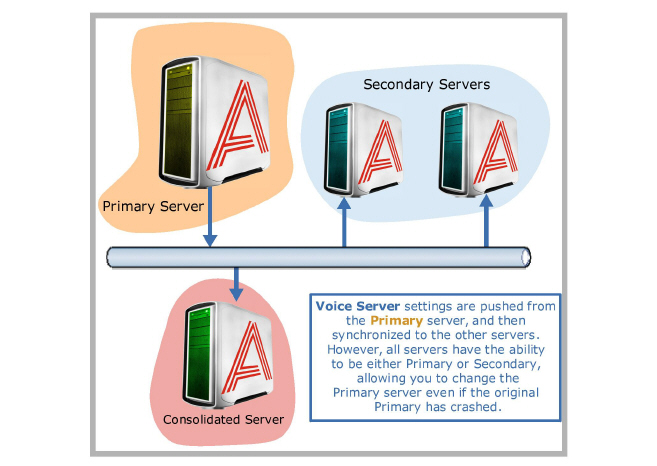
Voice Server Settings and Primary Server Selection
While many of the settings are controlled by Consolidated server, Voice Server settings within Messaging admin console is managed by the Primary Server. Each Voice Server, including the Primary and all Secondary Servers, will have its own entry within the Voice Server settings section. Only the Primary Server will be able to modify the fields within Voice Server settings, which is then pushed and synchronized to all other servers. However, all servers are able to change a single field labeled Primary within the Voice Server settings. This field can be used to designate any Voice Server as the Primary Server. If your Primary Server is unavailable for any reason (e.g. taken offline for maintenance), you will be able to assign another Voice Server as a Primary should the need arise.
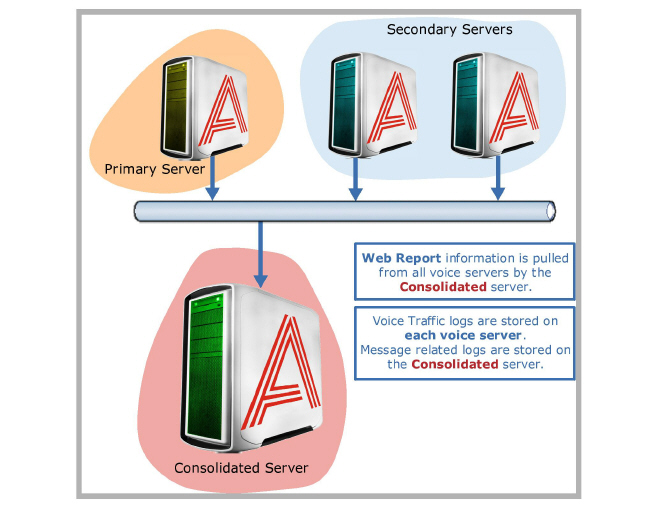
When it comes to voice traffic, each Voice Server will store activities which have occurred on that server, which means that logs related to a call will only be available on the specific server that the call took place (both incoming and outgoing). All message related logs (including voice messages) will be stored on the Consolidated server since it is the Consolidated server’s task to maintain synchronization of messages.
If you wish to create a Web Report of server activities, the necessary information will be pulled by the Consolidated server from the Voice servers. For most purposes, all you have to do is connect to Web Report services within the Consolidated server to obtain comprehensive information regarding the usage and status of your server. Individual log files are mostly used for troubleshooting purposes, so you will not have to track them from each servers separately.
An Avaya Messaging HA installation can be spread across a geographically distributed network. Geo Redundancy allows a section of the network in one part of the world to go offline without affecting the remaining elements.
Installing Messaging with Geo Redundancy proceeds the same way as it does with any other HA install, but with some of the servers existing in other locations.
Geo Redundancy has the following network connection requirements to operate properly.
•All Messaging servers must be on the same network as the PBX.
•All servers must have a minimum 1Gbps connection to the network.
•The maximum round-trip latency for optimum performance is 10ms between servers, with an acceptable tolerance up to 60ms.
•The maximum round-trip latency between the voice servers and the PBX must be no more than 200 ms.
•Optimal round-trip latency is a maximum of 150 ms.
•The path of connectivity must have 20Mbps guaranteed bandwidth with no steady-state congestion.
•At all times, the LAN network connection must provide a min guaranteed 20Mbps upload / download speed.
Contact your dealer if you have any further questions.